Biometrics and Machine Learning Group
Latest news
February 2025: conference proceedings - Rasel Ahmed Bhuiyan, Mateusz Trokielewicz, Piotr Maciejewicz, Sherri Bucher, Adam Czajka. "Iris Recognition for Infants" Proceedings of the Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) Workshops, February 2025, pp. 83-92.
December 2024: journal papers - Mateusz Trokielewicz, Piotr Maciejewicz, Adam Czajka. "Post-mortem iris biometrics – Field, applications and methods." Forensic Science International, Volume 365, 2024, Article 112293. ISSN 0379-0738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j .forsciint.2024.112293.
April 2024: journal papers - Adrian Kordas, Ewelina Bartuzi-Trokielewicz, Michał Ołowski, Mateusz Trokielewicz, "Synthetic Iris Images: A Comparative Analysis between Cartesian and Polar Representation" 2024, Sensors, 24(7), 2269, https://doi.org/10.3390/ s24072269
We are pleased to announce that Weronika Gutfeter defended her doctoral dissertation on face recognition based on multi-shot images using deep aggregation networks, supervised by prof. Andrzej Pacut, on the 18th of May, 2023.
Iris Localization using Active Contours
Method proposed by W. Gutfeter in her engineering dissertation (under supervision of A.Czajka) was a step toward creating more accurate iris localization algorithm. In comparison to the classic methods deriving from the Daugman's algorithm [1], iris contours were modelled by the closed curves and not by the circles. Estimation of contours was conducted using Level Set approach introduced by Osher and Sethian in [2].
For each image of the eye an array with actual values of the level-set function φ was created – so called φ-map. It was assumed that the contour leads through the points at which φ function changes its sign (0-level set). Initial positon of contour was established as a circle laying inside the area of the pupil. Then values of the φ-map were updated iteratively according to the procedure described by the equation.
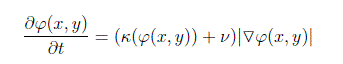
where ν and κ are additonal parameters of the evolution (speed and curvature).
Update causes the contour to move toward a desired position – they should be attracted by the areas in the image with a high gradient of the intensity. By fine-tuning the parameters of update function the shape of the contour could be controlled – it can be more elastic or more circle-like. One of the improvements introduced in the project was to process the image in the coarse-to-fine strategy: resolution of the image was increased while approaching the final solution.
Method was evaluated on modified Bath Iris Database with hand-drawn masks for iris and pupil. It gained almost 3 times higher accuracy (defined by the common geometric area of the result and the reference mask) than other two methods based on Daugman's algorithm.
Publication
W.Gutfeter, "Lokalizacja tęczówki metodą Aktywnych Konturów (eng. Iris localization using Active Contours)", engineering thesis, supervisor: A. Czajka, 2010, Warsaw University of Technology